Advanced segments are awesome because they provide ways to segment traffic based off premade data or custom segments. They don’t need regex but still have that option and can be applied to historical data. Unlike filters they are not permanent. However, because they are applied after the pageview is tracked, they are visit-based not pageview based.
Advanced Segment vs Filters Quick Overview
When Google came out with advanced segments, they were all the rave. Before them, there was no easy way to segment historical data and compare segments against one another. Many thought advanced segments can replace filters, but there are key differences. Google has a great support page explaining the differences, but here is a quick recap of top 5 differences:
- Google Analytics advanced segments allow you to segment historical data, filters start when they are first created and thus do not incorporate historical data
- Advanced segments are not permanent and don’t alter the inflow of web traffic data, filters do
- You can compare up to 4 advanced segments against one another
- Advanced filters allow for more complicated data manipulation, such as always showing a certain branded search term as direct traffic
- Fliters are pageview based and advanced segments are visit-based
What does visit-based mean?
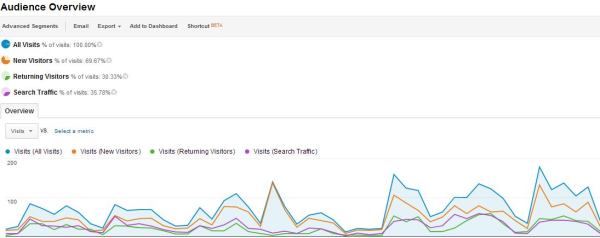
Being visit-based means that advanced segments only filter web traffic on a visit level, so if any attributes of a visit match the segment settings/parameters set, the advanced segment will kick in. For example, if you set a filter to include traffic to a certain page (we’ll say infotrustllc.com/events), then the filtered profile Content-All Pages report will only show traffic to that page, since an include filter means include only.

However, if you create an advanced segment for the same thing, include traffic to infotrustllc.com/events, you will still traffic to other pages in the Content-All Pages report.
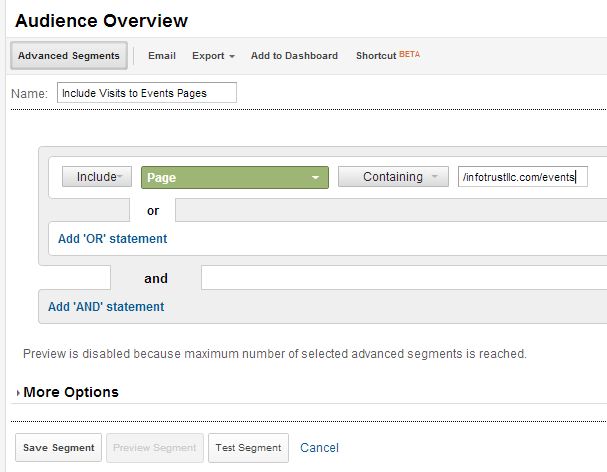
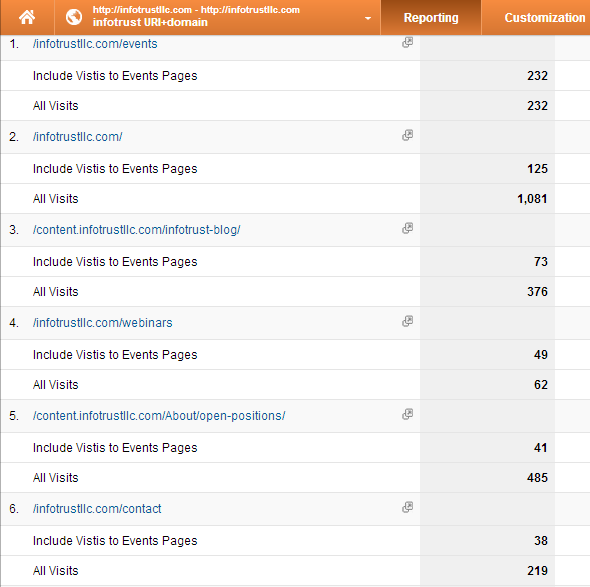
So why does this happen? Since advanced segments are visit-based, any engagement that occurs during a session still shows as long as they went to that specified page at least once. So say I go to I go to our homepage (infotrustllc.com), then to our blog (infotrustllc.com/blog), then to the events page (infotrustllc.com/events), then to the contact page (infotrustllc.com/contact) then I leave the site. With the advanced segment described above (Include -> page -> infotrustllc.com/events), my reports would show my full visit session, including all other pages I hit during that session.
On the other hand, if I never navigated to the events page during a session (say homepage->blog->contact then leave the site), that session would not be shown, since the events page was never hit.
So why does this matter?
After using Google Analytics for more than a year on a daily basis, I start to notice little discrepencies (or what I thought to be so) in the reporting. Understanding the different ways advanced segments and filters segment the web traffic data can help a lot when analyzing the reports. The biggest mistake any marketer or organization can make is misinterpreting the data and making bad marketing decisions. By knowing how and when certain data will be shown can help improve overall analysis and therefor improve the marketing dollars you spend in the digital space.
I hope this was a helpful quick tip about advanced segments but feel free to reach out to us if you have any questions, concerns or want help setting up your Google Analytics!
Article Written by Amin Shawki


