Authorization is the first step of managing and accessing your account data through the Google APIs. There are a number of ways for your application to authenticate. For this example we will demonstrate how you can use the Java Client Library to access your GTM and GA accounts.
Official documentation can be found here.
Auth Types
Accessing the API requires some form of an authentication key. You can either use a service account key, for server to server interactions, or an oauth client ID to gain access for a specific user.
Service Account
A google service account is used as a way to provide access to your data to support server to server interactions. This is useful when you are creating a new application and setting up a tie-in to Google Tag Manager or Google Analytics. You will need grant access to this service account.
User Account
If your application needs to act as the user, OAuth will allow them to login using their Google credentials. Browser OAuth is where your application will open a web browser to login using their own Google account to grant access to Google Tag Manager or Google Analytics.
In the case that you need your application to act as a different user, another way we can authenticate is by having the user provide their JSON key along with an authorization token.
NOTE: This provides you complete access to act on behalf of the other user utilizing the API. This should be done VERY carefully and with caution. In most cases where you feel you should do this, you should first see if it’s possible to use a service account instead.
Setting Up a Project
The first step is getting your project setup. This section outlines creating the project and then creating an OAuth Client ID or Service Account Key for the project, based on your needs.
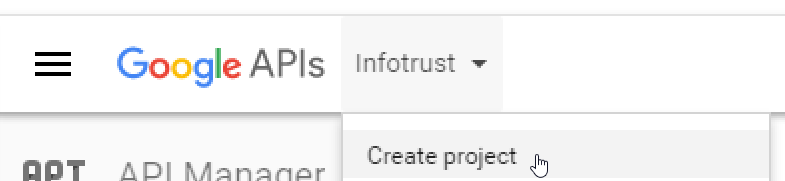
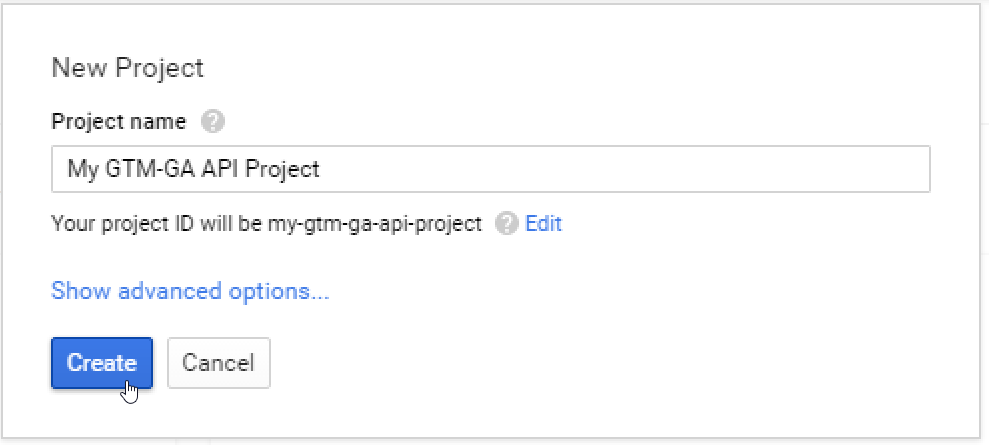
Create a project
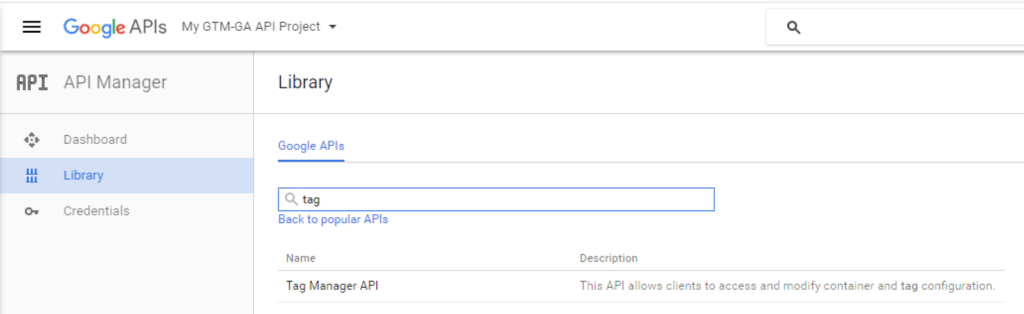
Enable Google Analytics and Tag Manager APIs in the Library Menu
1) Search for Tag Manager, Click Tag Manager API, Click Enable
2) Repeat for Analytics API
Create an OAuth Client ID or Service Account Key
OAuth Client ID
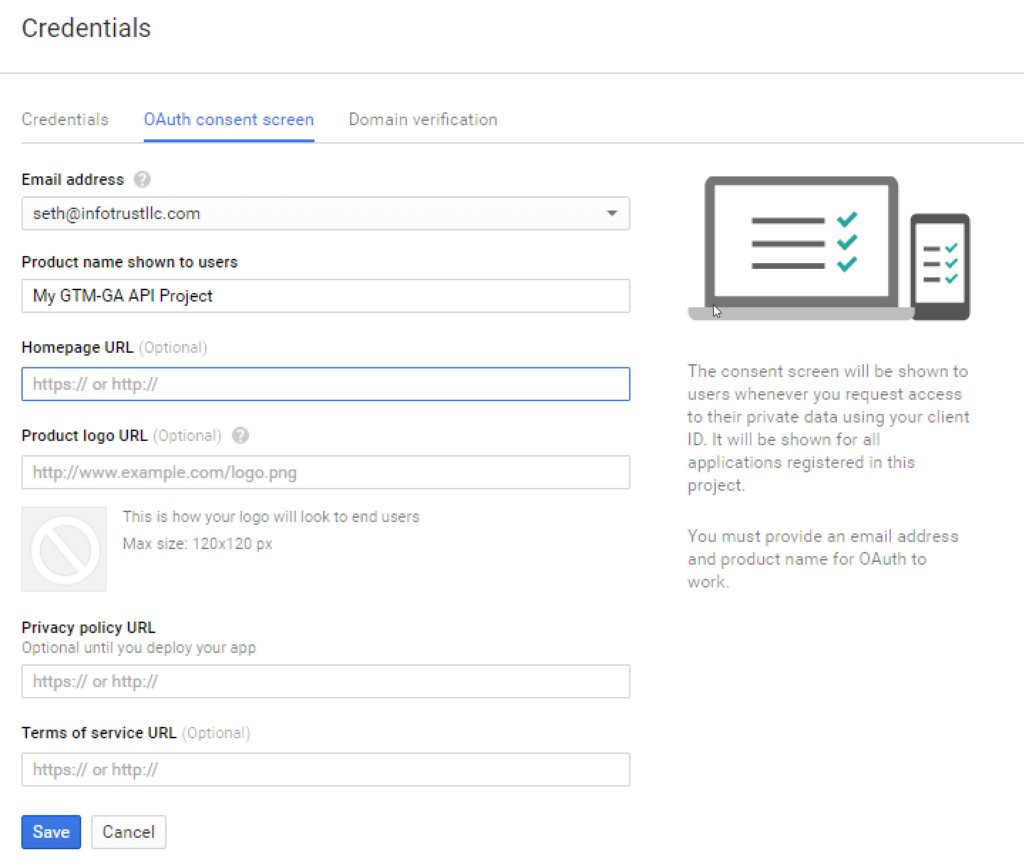
Configure Consent Screen
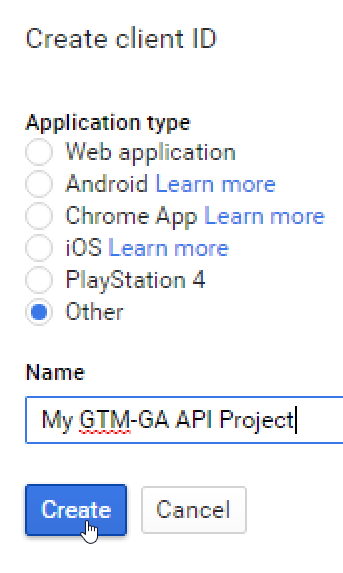
For using the Java SDK, we’ll select ‘Other’
It will then show you your client ID and client secret. You can ignore these because we’ll download the JSON file in a moment.
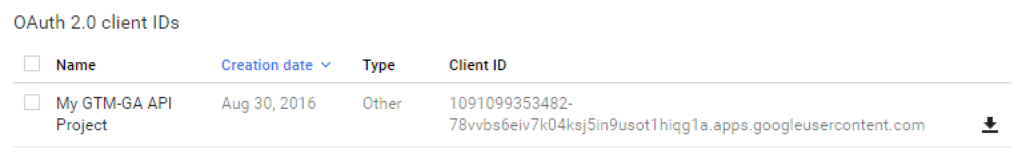
Click the download icon next to your client ID to download the json file. Put this file into the GoogleAPIAuthExample/authkeys folder.
Service Account Key
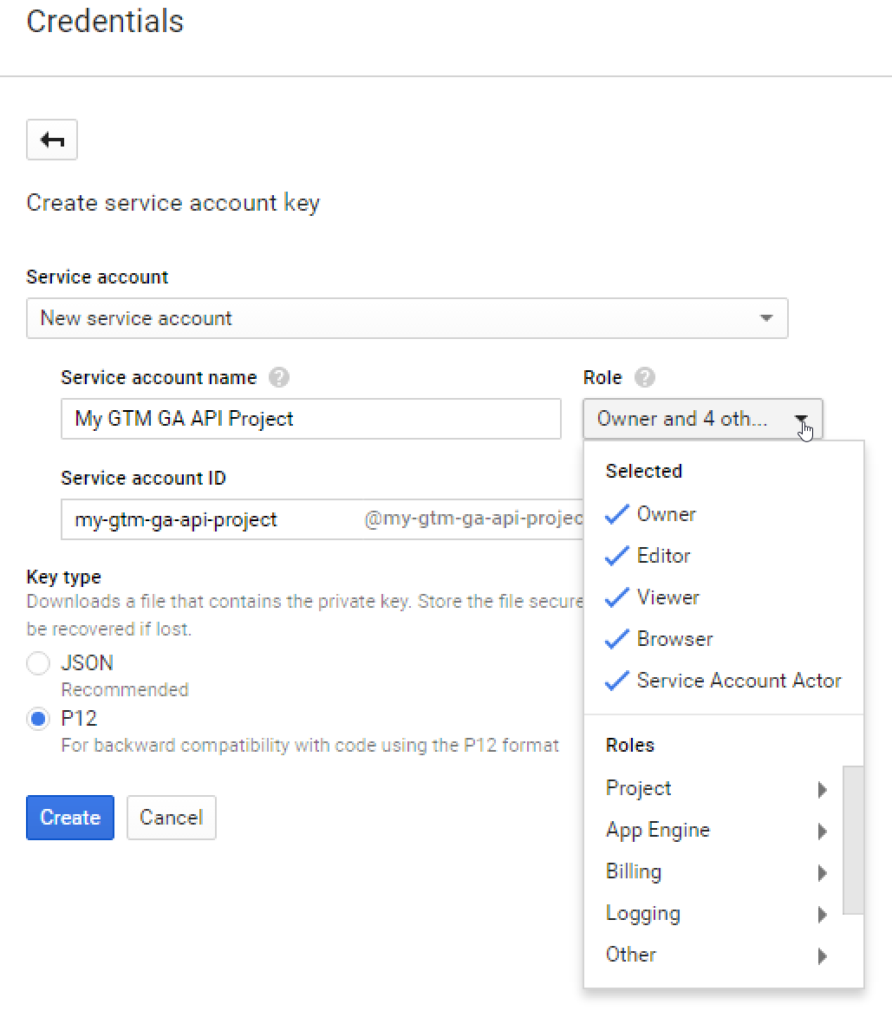
Be sure to Specify P12 Key Type
Download your p12 key into the GoogleAPIAuthExample/authkeys folder
Get your service account id from the Manage Service Accounts Page and take note of this for later.
Setup Options
- DataStore Path: This is the folder where your authorized credentials will be stored. If this file is deleted it will require the user to reauthenticate.
- Application Name: The name of your application.
- P12_AUTH_KEY_FILEPATH or JSON_AUTH_KEY_FILEPATH is used to specify the relative location of your auth key.
- SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL: If you are using a service account, this is the constant you need to specify the service account ID in. It should have similar suffix to “@iam.gserviceaccount.com”
Service Account Auth Usage
private static Credential authorizeServiceAccount() throws Exception {
// Construct a GoogleCredential object with the service account email
// and p12 file downloaded from the developer console.
HttpTransport httpTransport = GoogleNetHttpTransport.newTrustedTransport();
GoogleCredential credential = new GoogleCredential.Builder()
.setTransport(httpTransport)
.setJsonFactory(JSON_FACTORY)
.setServiceAccountId(SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL)
.setServiceAccountPrivateKeyFromP12File(new File(P12_AUTH_KEY_FILEPATH))
.setServiceAccountScopes(AnalyticsScopes.all())
.build();
return credential;
}
Token + JSON Auth Usage
private static Credential authorizeWithAccessToken() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
// Load client secrets.
GoogleClientSecrets clientSecrets = GoogleClientSecrets.load(JSON_FACTORY,
new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(JSON_AUTH_KEY_FILEPATH)));
//Specify which scopes are enabled.
List gaGTMScopes = new ArrayList();
gaGTMScopes.addAll(AnalyticsScopes.all());
gaGTMScopes.addAll(TagManagerScopes.all());
// Set up authorization code flow for all auth scopes.
GoogleAuthorizationCodeFlow flow = new GoogleAuthorizationCodeFlow.Builder(httpTransport, JSON_FACTORY,
clientSecrets, gaGTMScopes).setDataStoreFactory(dataStoreFactory).setAccessType("offline")
.build();
StoredCredential scred = flow.getCredentialDataStore().get("user");
if (scred != null) {
GoogleCredential cred = new GoogleCredential.Builder().setTransport(httpTransport)
.setJsonFactory(JSON_FACTORY).setClientSecrets(clientSecrets).build();
return cred.setAccessToken(scred.getAccessToken()).setRefreshToken(scred.getRefreshToken());
} else {
String url = flow.newAuthorizationUrl().setRedirectUri(clientSecrets.getDetails().getRedirectUris().get(0)).build();
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); // Reading from System.in
System.out.println(url);
System.out.println("Enter access token: ");
String accessToken = reader.next();
reader.close();
// Authorize.
GoogleTokenResponse response = flow.newTokenRequest(accessToken)
.setRedirectUri(clientSecrets.getDetails().getRedirectUris().get(0)).execute();
return flow.createAndStoreCredential(response, "user");
}
}
Browser OAuth Usage
private static Credential authorize() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
// Load client secrets.
GoogleClientSecrets clientSecrets = GoogleClientSecrets.load(JSON_FACTORY,
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream(JSON_AUTH_KEY_FILEPATH)));
// Set up authorization code flow for all auth scopes.
GoogleAuthorizationCodeFlow flow = new GoogleAuthorizationCodeFlow.Builder(httpTransport, JSON_FACTORY,
clientSecrets, AnalyticsScopes.all()).setDataStoreFactory(dataStoreFactory).build();
// Authorize.
return new AuthorizationCodeInstalledApp(flow, new LocalServerReceiver()).authorize("user");
}