Google Analytics 4 provides comprehensive insights into the user journey, combining website and app experiences into a single platform. It helps businesses understand their customers and make informed decisions to improve performance.
In this article, we will delve into the disparities between GA4 and Universal Analytics (previously referred to as Google Analytics 3) to gain a comprehensive understanding of customer actions on both web and app platforms. Don’t miss out on this advantage for your business.
Google Analytics 4 vs. Universal Analytics
Google Analytics 4 aims to address some of the concerns raised in Universal Analytics and introduce new concepts that are both scalable and adaptable. Here are the key differences:
1. Data Processing: Session vs. Event-Based Model
Universal Analytics’ session based model is complex and requires significant computation to manage. Merging unstructured or semi-structured data with structured data can be difficult, and storing and querying large amounts of data without losing information is crucial. However, data collected through cookies can result in data-gaps and non-compliance with emerging data privacy policies like CCPA and GDPR.
Google Analytics 4 addresses this problem with an event-based schema solution where everything is an event. As a result, GA4 processes the user’s event as a stand-alone model with its unique parameters, ensuring that its database is flexible, scalable, and super-fast when queried.
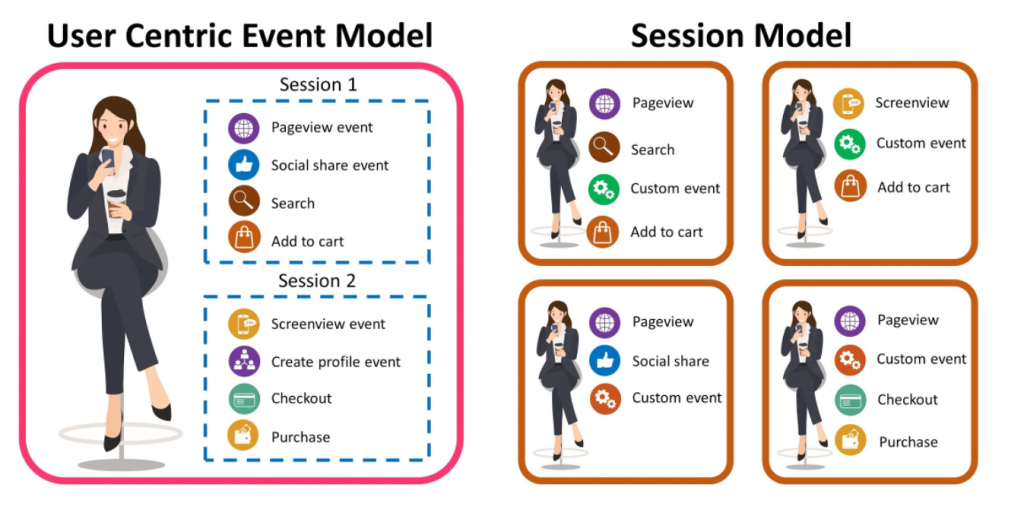
[Editor’s note: Want to learn more about the event model used by the properties? Go to this article for an overview.]
2. Audiences Definitions
GA4 offers a plethora of audience capabilities that far surpass Universal Analytics. With a wider selection of dimensions and metrics for audience definition, users can easily optimize their remarketing efforts. GA4’s machine learning technology generates prebuilt predictive audiences based on user data that can be marked for conversions, maximizing the potential for success. Additionally, the platform’s integration with Google Marketing Platform ensures that users with Ads Personalization enabled receive marketing ads on multiple devices.
3. Identity Specs for Reporting
The reporting capabilities for cross-device and platform usage in Universal Analytics are limited. Only User ID-enabled views provide this feature, and even then, it only uses the User ID for generating cross-device reports. Google Signal reports are available in non-user ID views, but they are restricted within UA.
GA4 takes a different approach as it is a cross-device property that prioritizes a user-centric approach. This approach combines classic User ID, data from Google Signals, and Device ID to provide information across all reports. Furthermore, it allows for de-duplication and rollup so that a user’s journey across various platforms can be viewed. With this, you can answer questions about your users regardless of platforms, such as “How much revenue did a user generate, regardless of the device category?”
4. Custom Tracking
Custom dimensions in Universal Analytics are not primary dimensions for analysis but rather secondary dimensions on top of standard reporting. However, in Google Analytics 4, custom metrics are level-set with standard metrics for reporting and analysis in the “Explore” section of the UI. Additionally, GA4 automatically tracks additional events on both app and web, which benefits small businesses by providing key KPI reports such as Sessions and Total Users while saving costs from heavy implementation.
It’s worth noting that the number of Custom parameters varies per proper scope across GA4 free and 360 compared to UA, and there is no session scoped parameter. Therefore, it’s essential to re-evaluate how to capture your Session scoped parameters in GA4 or determine of they are still needed.
5. Reporting UI
Universal Analytics has predefined Standard Reports that cannot be modified in the interface. Custom reports can be created to meet specific business needs, but they are only available to your instance unless you share the configuration. The limitation of dimensions and metric scope restricts analysis capabilities so users may need to focus on reporting and KPIs.
Google Analytics 4 offers customizable standard reports in the UI, allowing businesses to create unique reports tailored to their goals and KPIs. The Explorer section is also more powerful than in Universal Analytics, with machine learning at its core, empowering analysts to improve reporting.
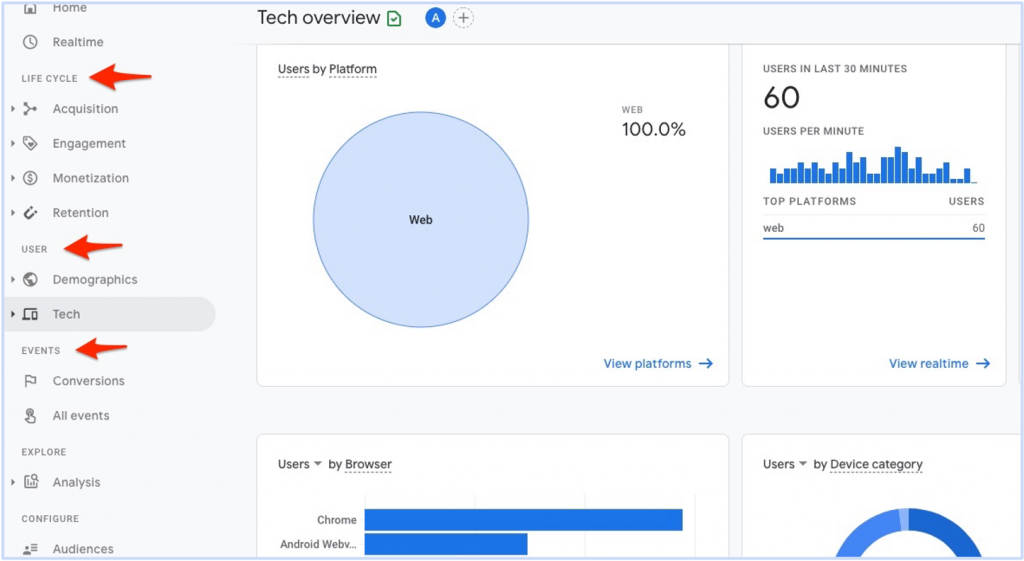
A few of the simplified reports in Google Analytics 4 include:
- Life Cycle Reports: Help you analyze data by the stage your customers are in their purchase journey.
- User Reports: Provide insights on user demographics and the technologies they use to navigate through your website.
- Business Objectives reports (optional): Similar to lifecycle report but there are Customized standard reports for GA4 properties that can be selected during setup.
[Editor’s note: If you are new to Explore reporting features, be sure to check out this article.]
Benefits of the new Google Analytics 4 Event-Modeled Property
Some advanced technologies, such as machine learning algorithms, have been used to create Google Analytics 4. The benefits you can enjoy include:
1. Adaptability and Data-Driven Decisions
As technology continues to advance rapidly, there are growing concerns regarding user privacy. However, GA4 has addressed this issue by utilizing machine learning and behavioral modeling to generate modeled data for non-consenting users as part of the reporting identities. This approach helps fill gaps in data while still respecting user privacy. Moreover, the insights provided by GA4 across different devices and platforms are more accurate and can better represent customers, ultimately supporting marketing goals.
2. Scalability
With GA4’s event-based schema, merging App and Web data is now easier than ever before. By making use of Google Signals and user ID from your CRM, GA4 allows you to gain a better understanding of user journeys. Additionally, you can now analyze KPIs across various platforms and devices without duplication, Moreover, GA4 offers new sampling controls to ensure accurate analysis.
3. Simplified, Organized, and Integrated Reporting
The introduction of data streams allows you to integrate app or website data into a single Google Analytics 4 property so that you have an aggregated view of your business. The reports are also less daunting and more intuitive so that it is easy to find insights by customer stage in the purchase life cycle and/or across devices and platforms.
4. User Properties
These are similar to user-scoped dimensions, but are only available from the moment they are set–but some of them are automatically collected. They also coexist with event parameters/custom dimensions and metrics, and are used to describe segments of your user base. You also have the ability to create your own unique user properties (25, for now) and use them in your report
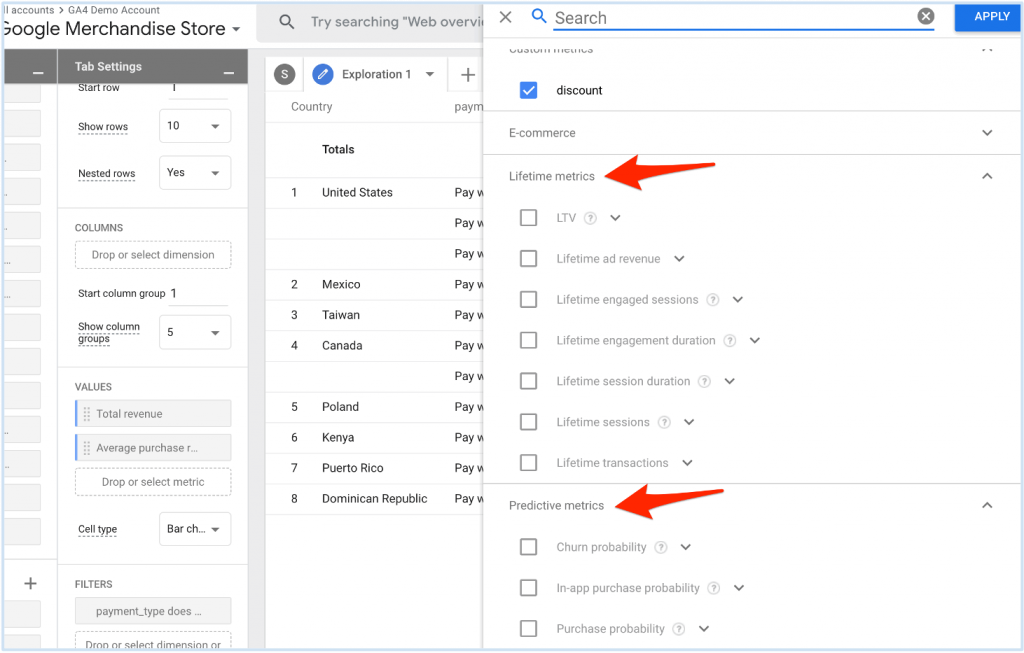
5. New Metrics and Dimensions
GA4’s new metrics and dimensions can add value to your analysis. For example, you can now see the potential revenue you could earn from a particular group of users. You can also see the churn probability to proactively push marketing budget into customer retention efforts.
Conclusion
As you can see, Google Analytics 4 can add value to your business. How?
- Its machine learning provides more meaningful insights for your business.
- Its reporting UI is simple, user-centric, and enables you to see the cross-platform user journey at any stage in the marketing funnel.
- Its event-based schema allows for a scalable, flexible, and a smooth user experience.
- It provides privacy-focused features for precise data control and PII minimization, along with other effective tools for businesses to obtain valuable insights.
If you are an existing Google Analytics user, set up a Google Analytics 4 property alongside your existing Universal Analytics property now to accumulate historical data and start benefitting from the new features of GA4.