Introduction
In the world of digital analytics, accurate and reliable data is crucial for understanding user behavior, optimizing marketing strategies, and driving business growth.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) offers a range of powerful features to help businesses make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. One such feature is Referral Exclusion, which plays a vital role in ensuring data accuracy and integrity.
In this blog post, we will explore what Referral Exclusion is, why it is important, where to find it in GA4, and best practices for its implementation.
So let’s jump right in!
What is Referral Exclusion?
Referral Exclusion is a feature in GA4 that allows you to exclude certain sources or domains from being attributed as referral traffic. When a user arrives at your website from a specific source or domain, it is typically recorded as a referral in your analytics reports. However, in some cases, you may want to exclude certain sources from being classified as referrals to provide a more accurate representation of user acquisition channels.
Why do we need it?
The need for Referral Exclusion arises from scenarios where the default referral tracking behavior in GA4 may lead to misleading or inaccurate data.
For example, consider we have an e-commerce business and during the process of a purchase (via a paid campaign) the user navigates to a payment gateway before they land on the thank you page.
In usual cases, this may mean that your conversions or transactions might end up being attributed to the payment gateway vs. the paid campaign. This is a very popular use case of Referral Exclusion.
Referral Exclusion helps address this issue by allowing you to define exclusion rules and ensure accurate attribution of traffic sources.
Where do we find it in GA4?
In GA4, you can configure Referral Exclusion settings within the Admin section of your property. To access it, follow these steps:
- Log in to your GA4 account and navigate to the Admin section.
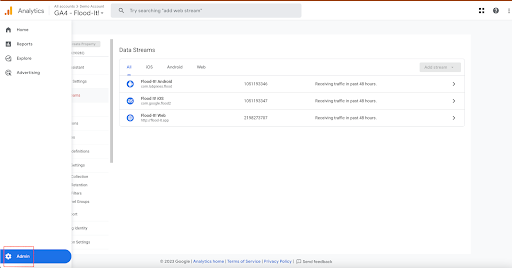
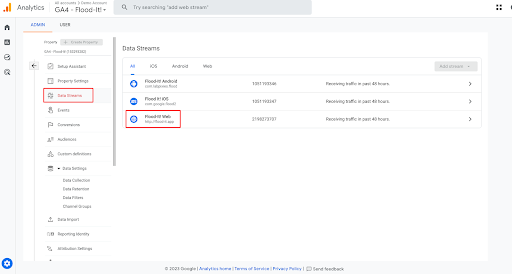
- Under the Property column, click on “Data Streams” and select the Data Stream you wish to update with Referral Exclusion.
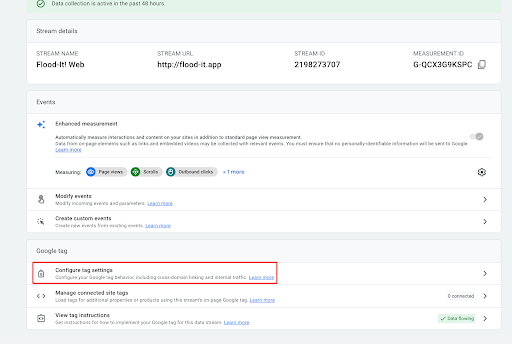
- Scroll down and select ‘Configure Tag Settings’.
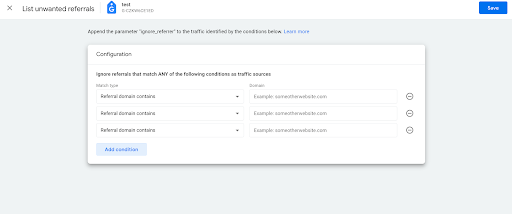
- Next, choose to ‘Show all’ the options and that is where you’ll find the ‘Unwanted Referrals’ option, which is essentially the same as GA4.
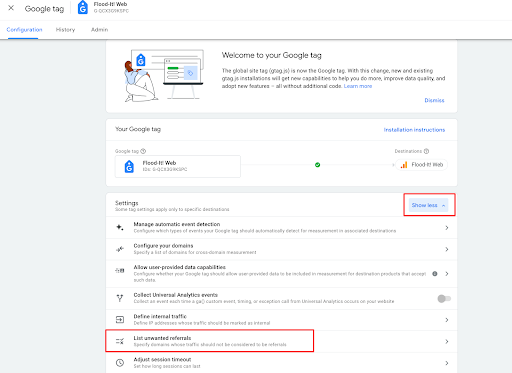
- This is where you add the domains you wish to count as ‘Internal Referrals’ or ‘Payment Gateways’ etc.
Best practices for Referral Exclusion
To make the most of Referral Exclusion and ensure accurate data analysis, consider the following best practices:
- Identify internal traffic sources: Before configuring Referral Exclusion, it is essential to identify and distinguish internal traffic sources from external ones. Internal traffic includes visits from employees, developers, or partners accessing your website for testing or development purposes. Excluding internal traffic from your analytics reports ensures that the data reflects genuine user behavior.
- Regularly review and update exclusion rules: As your website evolves, new traffic sources may emerge, while existing ones may change or become obsolete. It is crucial to periodically review and update your Referral Exclusion settings to align with your current marketing channels. Regularly auditing your exclusion rules helps maintain data accuracy and prevent unintended data loss.
- Test and verify exclusion rules: Once you have configured your Referral Exclusion settings, it is important to test and verify their effectiveness. Monitor your analytics reports closely to ensure that the excluded sources are accurately classified, and no relevant traffic is being unintentionally excluded.
Conclusion
Referral Exclusion is a powerful tool within GA4 that helps businesses maintain accurate and reliable data for effective decision-making. By properly configuring and managing Referral Exclusion settings, you can ensure that your analytics reports reflect the true sources of traffic.


