A primary area of compliance risk for most organizations is the data collection architecture on the website, specifically tags and pixels. While most people understand the few platforms they rely upon for analytics and media measurement are often collecting personal data, very few understand the full scope of data collection and sharing occurring. And with tag architectures that often look like the below, it’s hard to blame them.
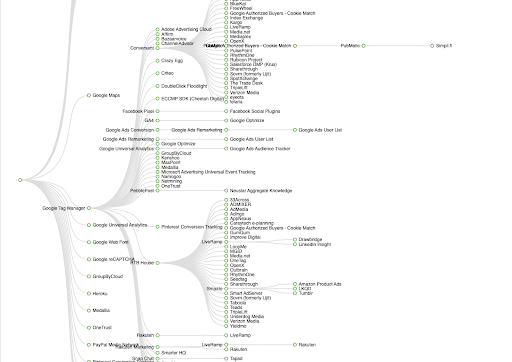
For businesses with consumers from California, this web of data collection, processing, and sharing can become an acute compliance risk due to CCPA requirements pertaining to the handling of any sale or sharing of personal information for behavioral advertising. When processing for these purposes occurs, the business must satisfy requirements for disclosure and opt-out. Failure to do so could result in a CCPA enforcement action.
To help organizations limit how personal information is used and effectively opt-out of any data which is shared for use in cross-context behavioral advertising, many platforms have introduced functionality for “restricted data processing”. When conditions for restricted data processing are implemented, analytics and advertising platforms will limit the processing of data to that which is not considered a “sale” or “sharing for cross-context behavioral advertising” per CCPA definitions. This ability thus allows for the collection of data for measurement use cases while respecting consumer opt-out requests and not selling nor using their data for the advertising platforms own purposes or targeted advertising.
Three commonly used platforms offer this functionality:
- Google Analytics
- Google Ads
- Facebook / Meta
Any websites using these technologies need to make sure settings are properly applied so that the personal information of site visitors is only being sold or shared in a compliant way and the activity is stopped as soon as the consumer opts-out.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is the most commonly used web analytics platform on the market. While many organizations simply use the platform to measure consumer behavior on their websites, there are a number of settings and capabilities that are often enabled which would put the collection and processing of data by Google Analytics in the scope of sale/sharing for CCPA. It is important to be aware of these settings and, if in use, to ensure proper disclosures of the sale/sharing behavior are made as well as to set up the architecture to effectively opt consumers out of the behavior upon request.
Data Sharing Settings
Google Analytics provides the option to share your Google Analytics data with Google to help improve Google’s products and services. Enabling this option removes Google Analytics from the classification of “Service Provider” per the CCPA regulations because “A service provider shall not retain, use, or disclose personal information…for internal use by the service provider or contractor to build or improve the quality of the services it is providing to the business…” (CCPA Final Regulations Article 4.7050(a)). Thus when this setting is enabled Google Analytics is operating as a “third party” and the sharing of personal information with the platform would be considered a “sale” per the definitions in the CCPA.
Data Sharing Settings are at the account level in Google Analytics and are not able to be conditionally disabled at the user level. Therefore, this option should be disabled in the Google Analytics Account Settings to reduce compliance risk when using Google Analytics.
Google Ads Terms of Service
Also relevant for Google Analytics to function as a Service Provider are the Google Ads Terms of Service. These terms provide the certification that Google Analytics will operate as a Service Provider so long as restricted data processing conditions are met. To satisfy the CCPA requirement that this certification must be acknowledged with a written contract in place, the terms should be accepted in the Account Settings of your Google Analytics account. If contracting Google Analytics through a reseller, separate data processing terms with the sales partner are required.
Ads Personalization
Google Analytics provides the ability to create audiences for targeting from Google Analytics consumer behavior data. For example, an audience could be created for web visitors who viewed a particular product or added a product to a cart but did not purchase. When Google Analytics is linked with Google Marketing Platform (GMP) products, these audiences can be used for personalized targeting. When Ads Personalization is turned on within the Google Analytics property and the data is used in this way, personal information of consumers is being shared for purposes of cross-context behavioral advertising according to the CCPA.
In order to maximize the value able to be received from Google Analytics, it is recommended to properly disclose to the consumer the collection of their personal information for these use cases and to provide the ability to opt-out. Upon the consumers opt-out indication, Google Analytics should be configured to conditionally disable this functionality for the indicated user. We have written a separate guide that outlines options available for configuring Google Analytics 4 to satisfy these conditions.
Google Ads
All Google Ads platforms allow for the creation of audiences based upon observed user behavior on a site where the Ads tagging is present. This audience creation, when used for targeted advertising, would put the processing of the consumer’s personal information into the scope of “sharing” for the CCPA. It is important—whenever these platforms are in use and data is being used in this way—for the behavior to be disclosed to consumers and to give them the ability to opt-out. Again, restricted data processing for the Google Ads platforms can be used to stop the sharing behavior.
Enabling restricted data processing can be done in the Google Ads tags (when using Google Ads remarketing or conversion tagging on the site), within the Google Ads platform, or within other GMP platforms for data that is imported to Google Ads for advertising personalization.
Meta Pixel
Many websites advertise on Meta platforms (Facebook and/or Instagram) and use the Meta Pixel to measure campaign performance, as well as to send consumer behavior data to Meta which can be used for audience creation and targeting. With the default configuration of a Meta Pixel on a website, data collected is used for advertising personalization as well as for the improvement of Meta’s products. Therefore, with an out-of-the-box configuration, Meta is operating as a “third party” and the use of the Meta Pixel would be considered a “sale” of personal information for visitors from California. This must be disclosed and the consumer must be given the ability to opt-out of the sale and sharing for behavioral advertising.
To limit Meta’s use of collected personal information, restricted data processing options are provided through their Data Processing Options and Limited Data Use. This must be updated within the Meta Pixel script and then applied, at minimum, for all users who have opted out of the sale and/or sharing of their personal information.
Data collection on a website can be incredibly complex. A lot of platforms are often in use and many organizations don’t understand the true extent of what information is collected nor how it is used. This is not an excuse! To build a trusting relationship with consumers it is imperative to respect their privacy rights. Understanding exactly how data is processed and for what purposes across all platforms is the start. Setting up the data collection architecture using capabilities such as restricted data processing is the next step in getting to an optimal privacy-centric marketing data architecture.


